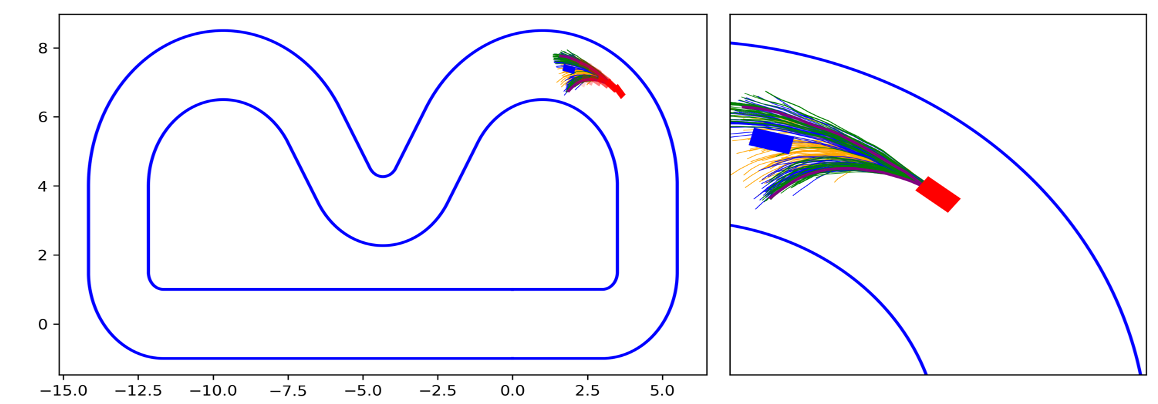
Iterative MPPI Car Racing
Undergraduate Thesis
This project focuses on solving the multimodal problem in sampling-based MPC(MPPI, Model Predictive Path Integral Control) in car-racing scenarios.
We can treat MPPI as a single-step diffusion process. Compared to the basic MPPI version which samples only 1 iteration in every step, applying iterative MPPI which updates the mean value according to the sampling result in last iteration would help avoid local minimum and improve sampling efficiency. However, when there are multiple feasible minimum values, iterative MPPI would suffer from the zig-zag between multimodal solutions in complex environment.
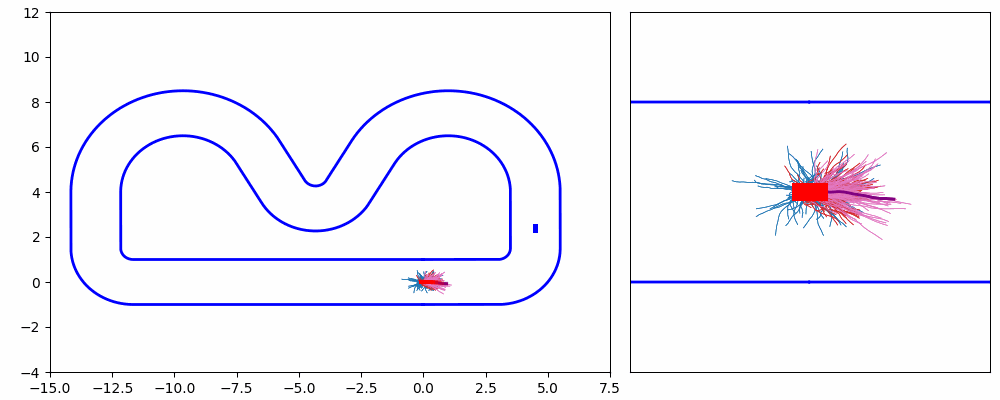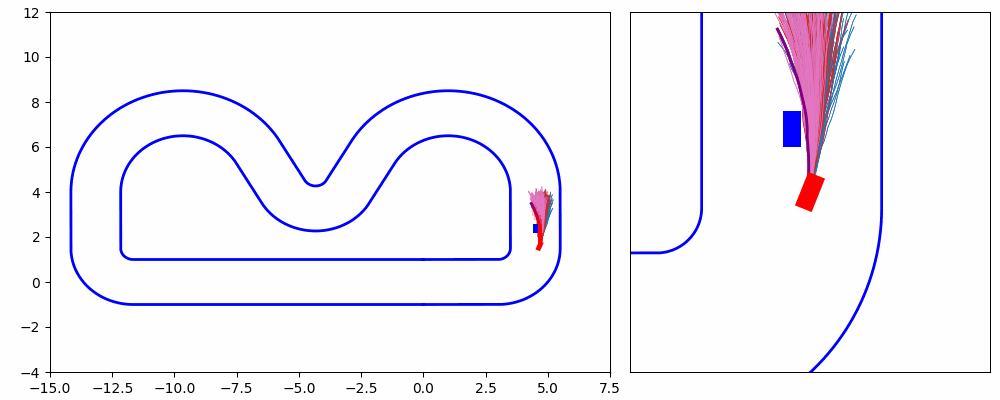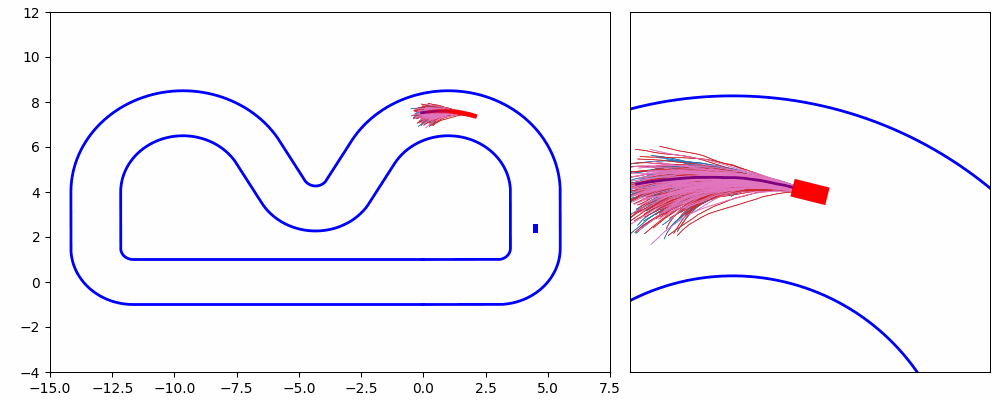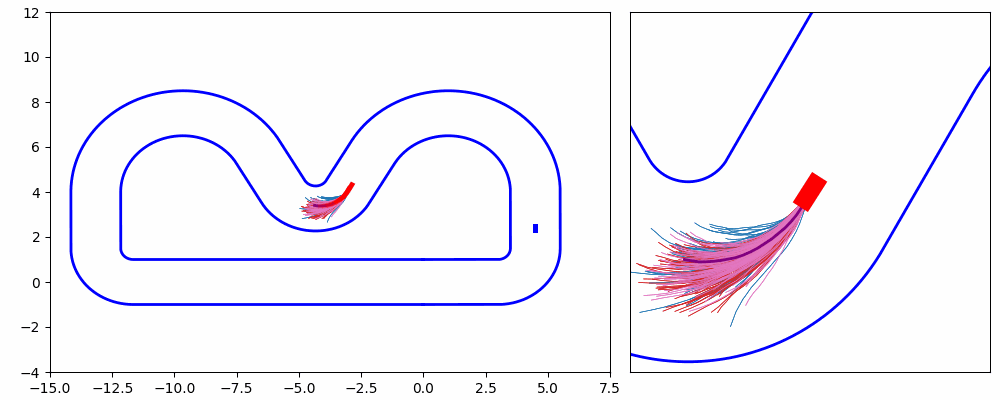
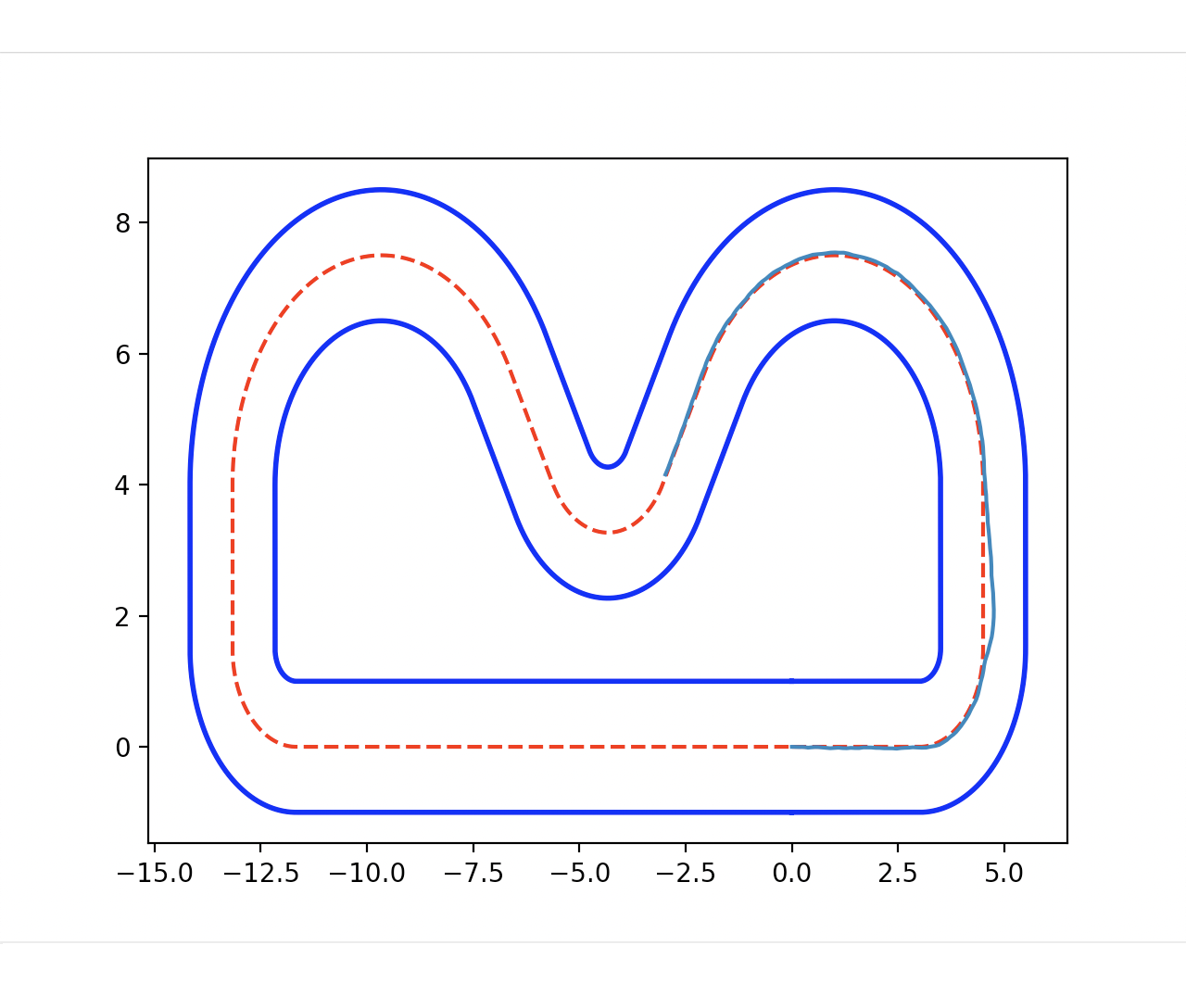
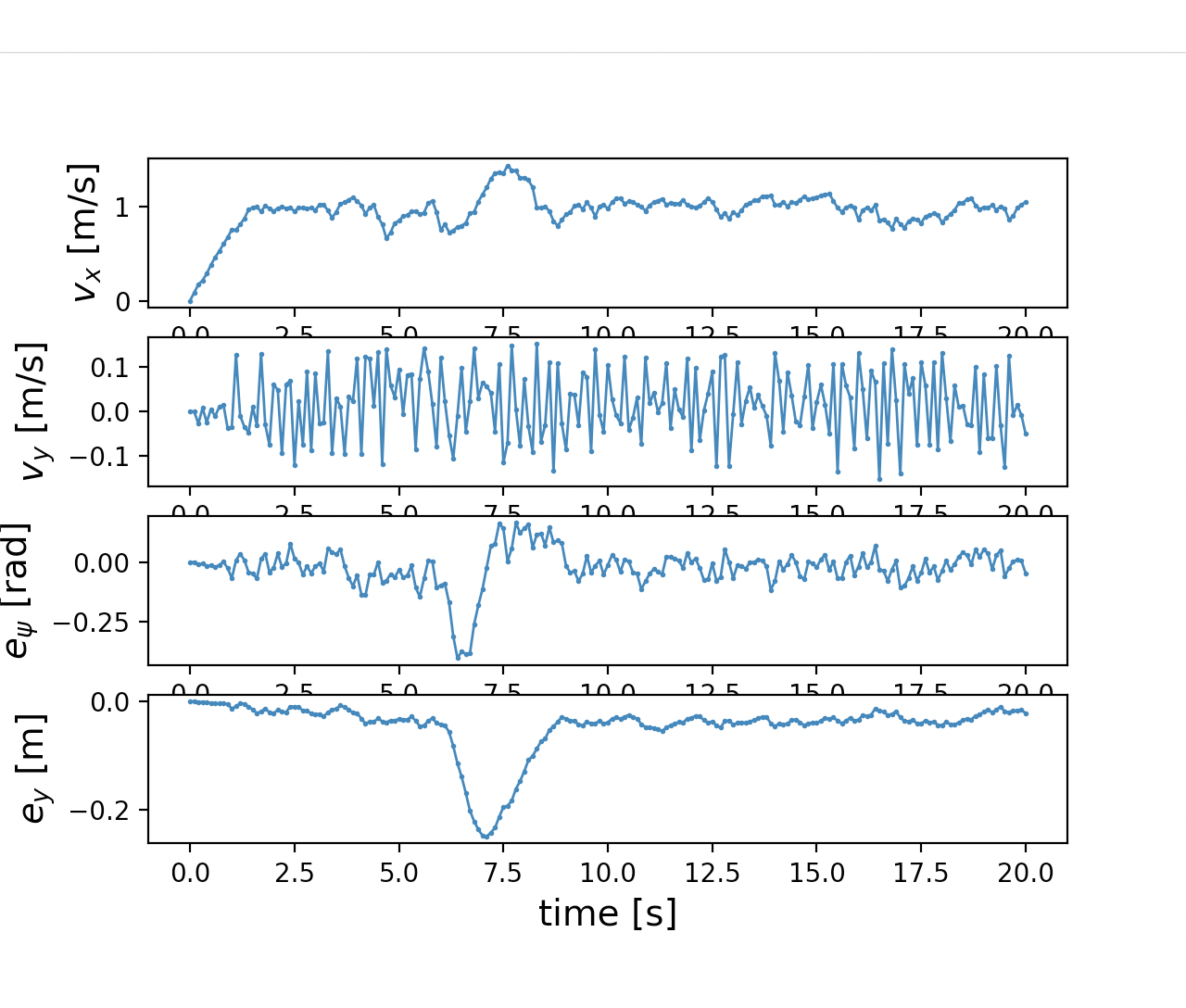
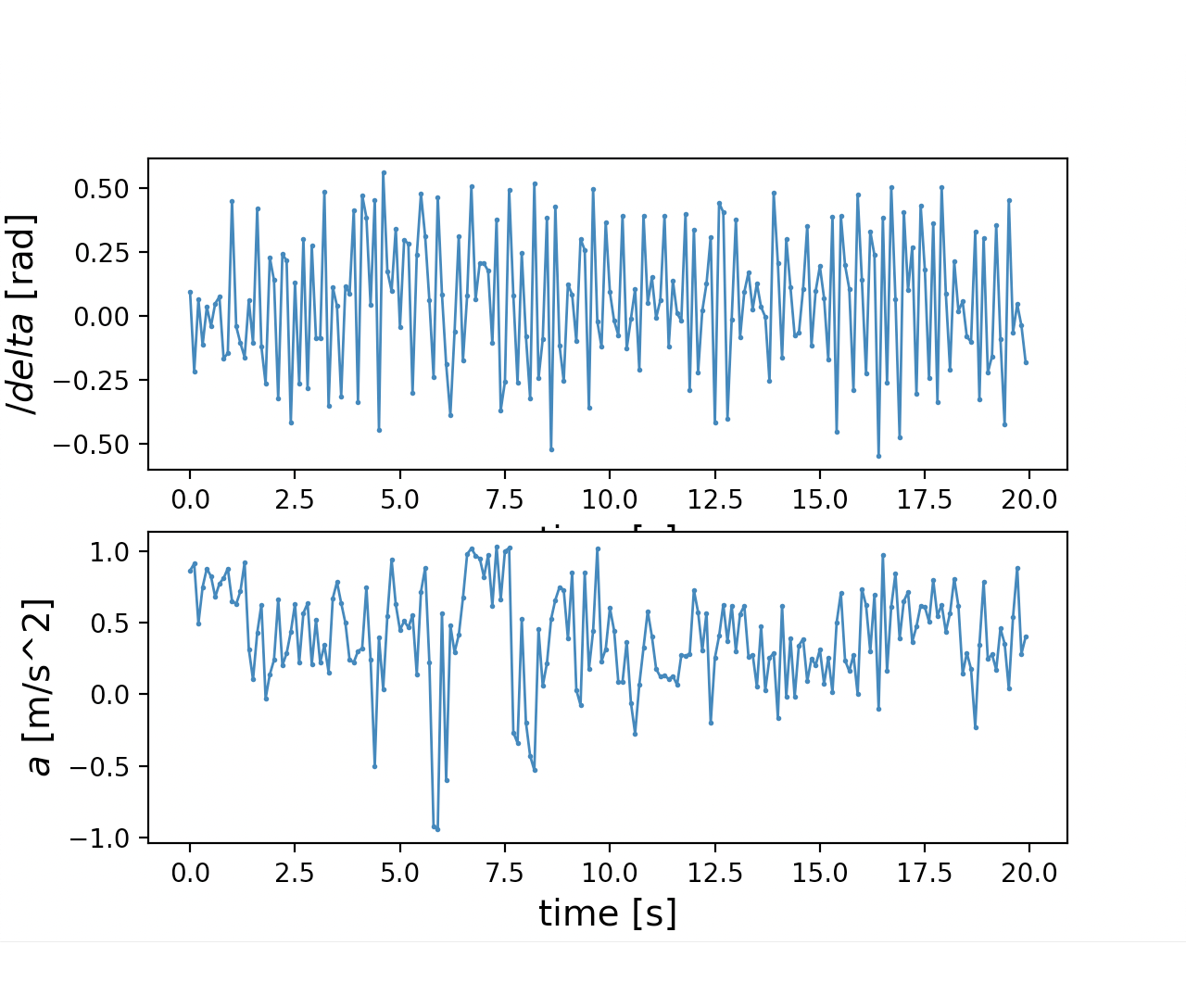
As shown in Figure 1 and Figure 3, the ego vehicle could overtake the obstacles either from the right or left side. Figure 3 shows that the vehicle could get stuck when the intention of overtaking keeps jumping between the left and right.
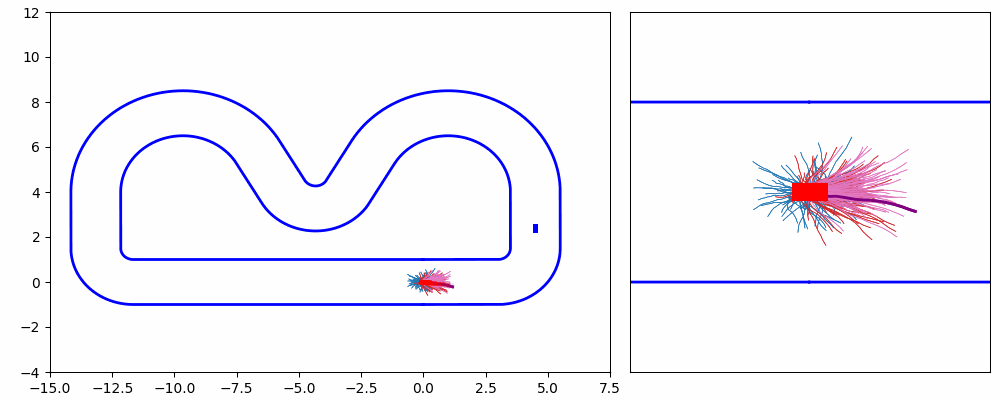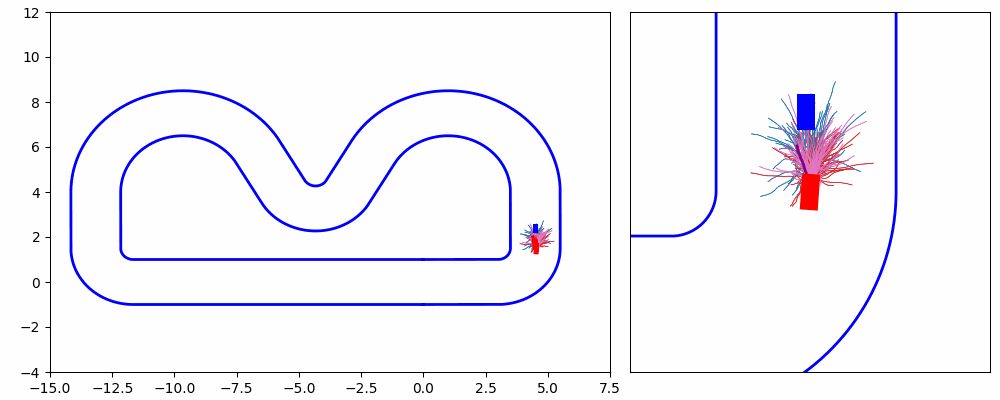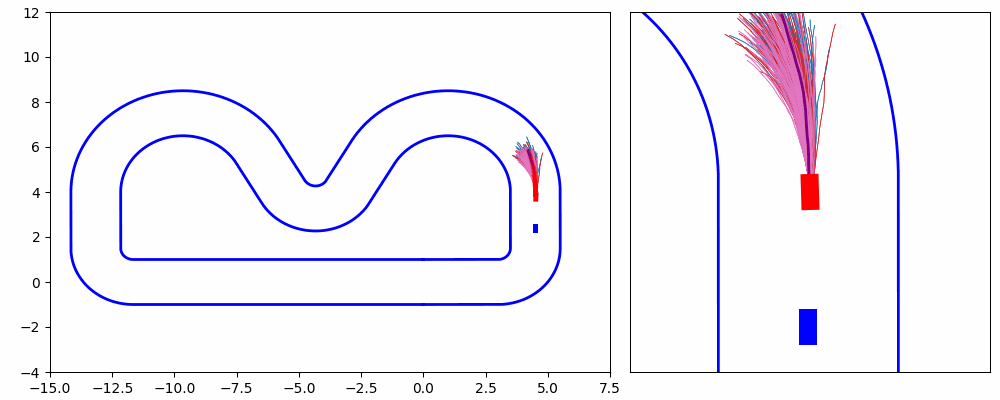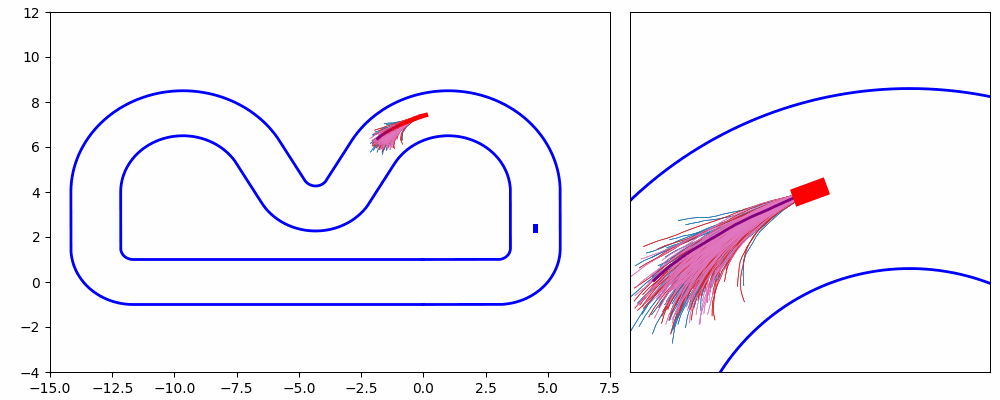
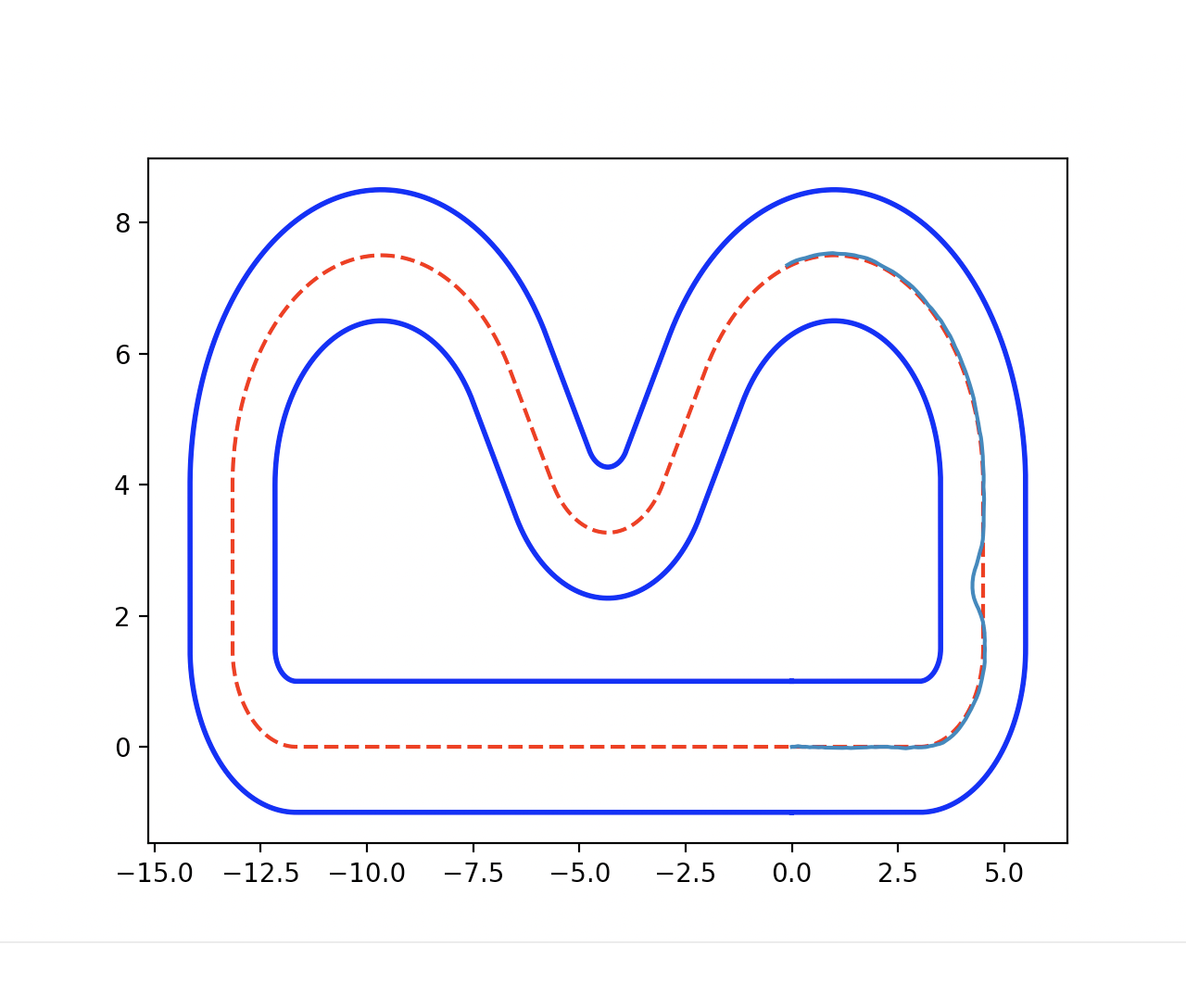
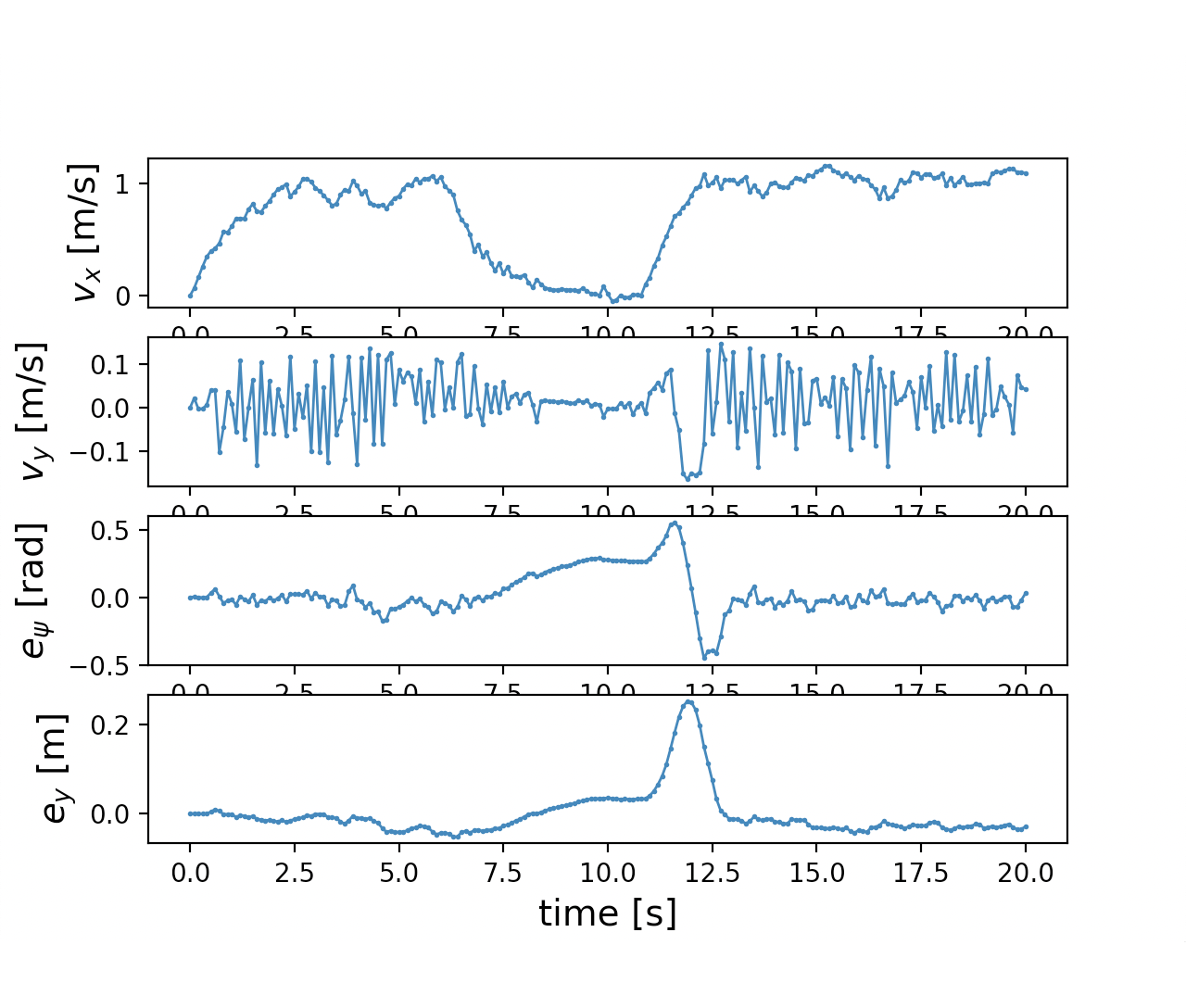
In this project, We propose an iterative MPPI framework with regrouping–resampling that unifies scenario generation, planning, and control, enabling the algorithm to automatically work out the overtaking tendency of static obstacles in car racing scenarios and bridging the planning process with trajectory generation, and solve the multimodal problem through maintaining a separate mean value and covariance matrix for each intention and pick the optimal solution with minimum efforts, as shown in Figure 5.